Suffering from both back pain and stomach pain can be incredibly uncomfortable and worrisome. In many cases, these two pains are related, as each can have a direct effect on the other. As an expert in medicine and the human body, I want to provide you with the information you need to understand why back and stomach pain might occur simultaneously and what steps you can take towards treating it. After reading this blog post, you’ll have more knowledge regarding your own health situation so that together we can move forward with finding solutions for reducing or eliminating your discomfort.
As a general rule, back pain and stomach pain can be symptoms of multiple medical conditions such as kidney stones, pancreatitis, or gastrointestinal ulcers. Chronic back pain can lead to postural changes that may cause digestive issues. Treatment may depend on the underlying cause and can include medication, chiropractic care, or surgery.
If you’re struggling with back pain, let me assist you in discovering some excellent office chair alternatives. With more than 30 years of experience in chiropractic practice and training in ergonomics, I’ve authored a book on posture, spoken on national TV, and engineered numerous solutions to enhance sitting comfort and posture. Furthermore, I have successfully crowdfunded a project for ergonomic seat cushions.
All Day Comfort & Support
The Connection Between Back Pain and Stomach Pain
The connection between back pain and stomach pain may seem surprising to some, but as a chiropractor, I can assure you that they can often be linked. The human body is an interconnected system, and issues in one area can sometimes manifest in another. There are several possible reasons why you might be experiencing both back and stomach pain, and understanding these connections can help you find the right treatment and relief.
Common Causes of Back and Stomach Pain
There are multiple potential causes for the co-occurrence of back and stomach pain. Some common causes include:
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Strained muscles or ligaments can lead to pain radiating from your back to your abdomen, or vice versa. Prolonged periods of poor posture, heavy lifting, or repetitive movements can strain these tissues and result in discomfort in both areas.
- Spinal Misalignments: Spinal misalignments, or subluxations, can lead to nerve irritation and pain. If the misaligned vertebrae are in the thoracic or lumbar regions, it could potentially cause pain in both your back and stomach.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: Certain gastrointestinal issues, such as indigestion, ulcers, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), can cause stomach pain that radiates to the back. In these cases, the pain is usually accompanied by other digestive symptoms, like bloating or gas.
- Kidney Issues: Kidney stones or infections can cause pain in both the back and the abdomen. The pain typically starts in the back and moves to the front as the condition progresses.
Chiropractic Care for Back and Stomach Pain
Chiropractic care can be an effective treatment for addressing the underlying causes of your back and stomach pain. As a chiropractor, I can assess your spine and musculoskeletal system to determine if misalignments or muscle strains are contributing to your discomfort. If spinal misalignments are identified, chiropractic adjustments can help realign the spine and alleviate nerve irritation. Additionally, we may suggest specific exercises and stretches to strengthen your core and back muscles, which can provide additional support and help prevent future pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While chiropractic care can help with many causes of back and stomach pain, it’s essential to recognize when it’s necessary to seek medical attention. If you’re experiencing severe pain, persistent vomiting, blood in your stool or vomit, or unexplained weight loss, these could be signs of a more severe issue that requires immediate attention. In such cases, it’s important to consult with your primary care physician or seek emergency care to address the potential underlying medical conditions.
Remember, understanding the connection between back pain and stomach pain is crucial to finding the right treatment and relief. As a chiropractor, I’m here to help you navigate through these issues and find the best approach to manage your pain.
Black Friday: 35% Off Today
Typical Delivery 1-3 Days
Stomach and Back Pain Together Female: Abdominal Pain, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, and Appendicitis
Stomach and back pain together in females can be attributed to several factors. Abdominal pain may arise from conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which is characterized by abdominal discomfort, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Appendicitis, an inflammation of the appendix, can also cause severe pain in the lower right abdomen that may radiate to the back.
Lower Stomach and Back Pain Together: Problems with Bloating, Bowel Syndrome, and Pancreatitis
Lower stomach and back pain together can be caused by bloating, which may result from gas, constipation, or overeating. Bowel syndrome, specifically irritable bowel syndrome, is another possible cause of pain in the lower stomach and back. Pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas, can cause severe abdominal pain that radiates to the back and is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and fever.
I’ve written a complete hands-on review about the best sitting position for sciatica, and here is what I tested best with my sciatica patients.
Bloated Stomach and Back Pain Female: Appendicitis, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, and Pancreatic Cancer
A bloated stomach and back pain in females can be caused by appendicitis, which typically presents with sharp pain in the lower right abdomen and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and fever. Irritable bowel syndrome is another potential cause, leading to abdominal discomfort, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Pancreatic cancer, although rare, can also cause bloating and back pain, along with other symptoms like jaundice, weight loss, and loss of appetite.
Upper Stomach and Back Pain at the Same Time: Pancreatitis, Pancreatic Cancer, and Abdominal Pain
Upper stomach and back pain occurring simultaneously can be indicative of pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas that causes severe abdominal pain radiating to the back, along with nausea, vomiting, and fever. Pancreatic cancer, although less common, can also cause upper stomach and back pain, in addition to other symptoms like jaundice, weight loss, and loss of appetite. Other causes of abdominal pain, such as gastritis or peptic ulcers, may also lead to upper stomach and back pain.
Pain in Lower Stomach and Back Female: Cancer, Appendicitis, and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Pain in the lower stomach and back in females can be attributed to various conditions, including cancer (such as ovarian or colon cancer), which may cause abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Appendicitis, an inflammation of the appendix, can lead to severe pain in the lower right abdomen that radiates to the back, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and fever. Irritable bowel syndrome is another potential cause, characterized by abdominal discomfort, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
Seat Cushion for Abdominal SupportAxial Ergonomic Seat Cushion® | Seat Chair Wedge
Quick Guide: A 30-Second Summary

All Day Comfort & Support
Product Name
Axial Designs™ Seat Cushion
Price
$149
Warranty
1 Year
Type
Posture Wedge
Top Layer
100% Natural Latex (Molded)
Bottom Layer
High-Density Foam
Top Material
Isometric Grippy Vegan Leather
Bottom Material
Non-Slip Material
Side Material
3D Breathable Fabric
Building an Ergonomic Seating Solution: Guidelines and Inspiration
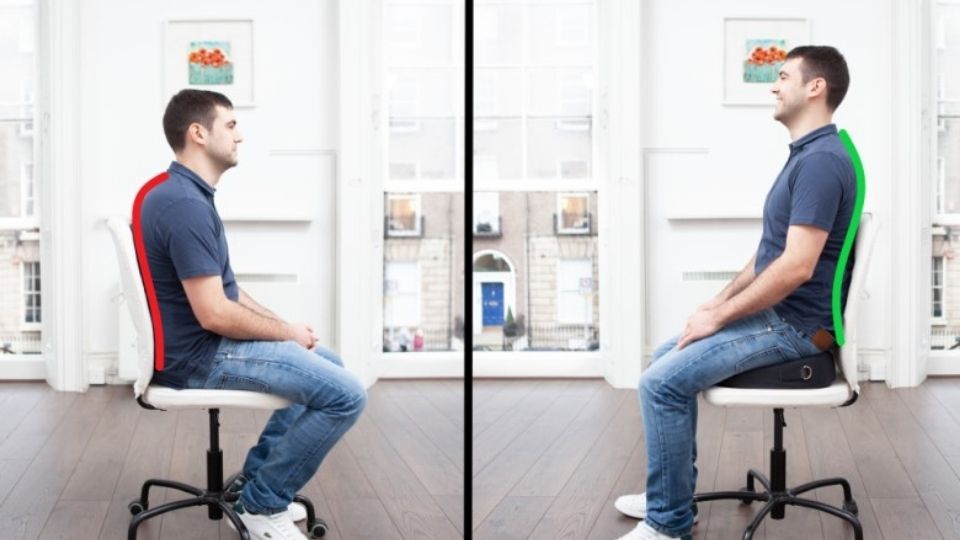
To optimally cater to your seating preferences, it’s crucial to pay attention to numerous factors, including the essential aspect of chair adjustment. There are several approaches to achieve this, like adding an ergonomic cushion and lumbar support. These features can reduce strain on your back and legs, enhancing comfort and posture during extended sitting sessions. Additionally, make certain your feet are firmly on the ground and there is ample clearance between your chair and workspace. By implementing these inspirations, any standard hard chair can be upgraded into an ergonomic retreat that supports long-term health and well-being.
Ergonomic Comfort Cushion
An ergonomic seat wedge (above) can be applied to align your spine correctly and foster balance. This top-quality natural latex comfort cushion helps fortify core muscles while alleviating tension in other body regions, such as the shoulders and neck. Moreover, sitting upright is gentler on your hips and knees, as it engages more muscle groups concurrently compared to resting back against something soft. This erect posture helps avoid the adoption of stress-producing habits that people may unconsciously develop while working.
Final Thoughts
While it is important to be mindful of back and stomach pain, it is not always indicative of a serious problem. However, if the pain persists, it is highly advised to contact a medical professional. Especially if the pain lasts more than three days or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, vomiting or shortness of breath.
Your family doctor can help you make the right decision in regards to diagnosis and treatment. The world of medical diagnoses is complex and ever-changing, so be sure to talk with a qualified health practitioner. When in doubt, seek a second opinion from another specialist. It’s always important to remember that you know your body better than anyone else– so take care of yourself with understanding and compassion. Ultimately the choice rests with you – listen carefully to your body and consult a professional for an expert opinion in times of need, but never cry wolf without being absolutely sure! Take responsibility for your own health and wellness with love, courage and a caring tone of voice.
Sources:
- Kristjánsdóttir, G., 1997. Prevalence of pain combinations and overall pain: a study of headache, stomach pain and back pain among school-children. Scandinavian journal of social medicine, 25(1), pp.58-63.
- Lépine, J.P. and Briley, M., 2004. The epidemiology of pain in depression. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 19(S1), pp.S3-S7.
- Reddy, Y.P., Senthil Kumaran, S., Vanka, V., Rab, A. and Patel, V., 2020. Abdominal pain–a common presentation with unusual diagnosis: a case report. Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives, 10(6), pp.604-608.
- Colombel, J.F., Shin, A. and Gibson, P.R., 2019. AGA clinical practice update on functional gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: expert review. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 17(3), pp.380-390.